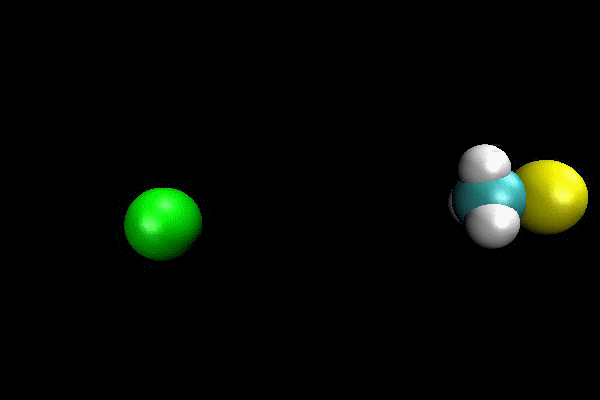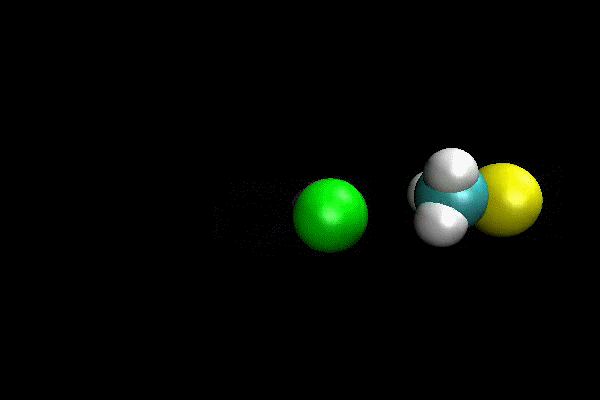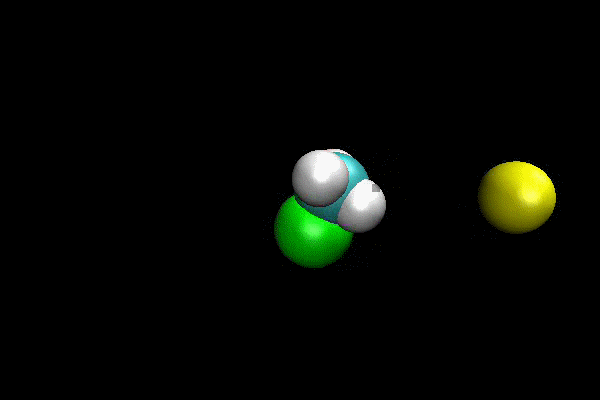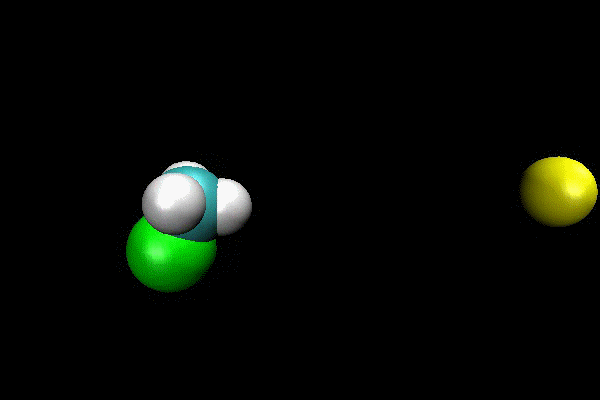Animation
Animation
Description
Cl- + CH3I ---> ClCH3 + I- SN2 Reaction
An ab initio MP2(fc)/aug-cc-pVDZ/ECP direct dynamics trajectory study was performed for Cl- + CH3I -> ClCH3 + I- reaction at reagent relative translation energy of 2 eV. The reaction dynamics are studied versus collision impact parameter b and the results show that reaction probability is quite low, and decreases as b is increased. By calculating maximum possible centrifugal barrier, the maximum impact parameter for reaction is estimated as 5.2 Å and the low reaction probability at larger b makes it computationally intractable to sample the complete range of b. However, important details of reaction dynamics are found. The reaction occurs by both direct and indirect mechanisms. The direct reaction occurs by traditional SN2 reaction path, with Cl- attacking backside of CH3 and directly displacing I-. The indirect mechanism occurs via a “CH3-rotation” mechanisms, where Cl- first strikes the side of CH3-group,causing it to rotate around more massive I-atom one or more times before Cl- reacts backside. For direct mechanism, the majority of energy is partitioned to product relative translation. The scattering is primarily backward with scattering angle within a small range. For indirect mechanism, the product energy is preferentially partitioned to CH3Cl vibration.
These animations were part of the research conducted by Bill Hase Research Group using HPCC resources.
High Performance Computing Center
-
Phone
806.742.4350 -
Email
hpccsupport@ttu.edu