EDYS Model
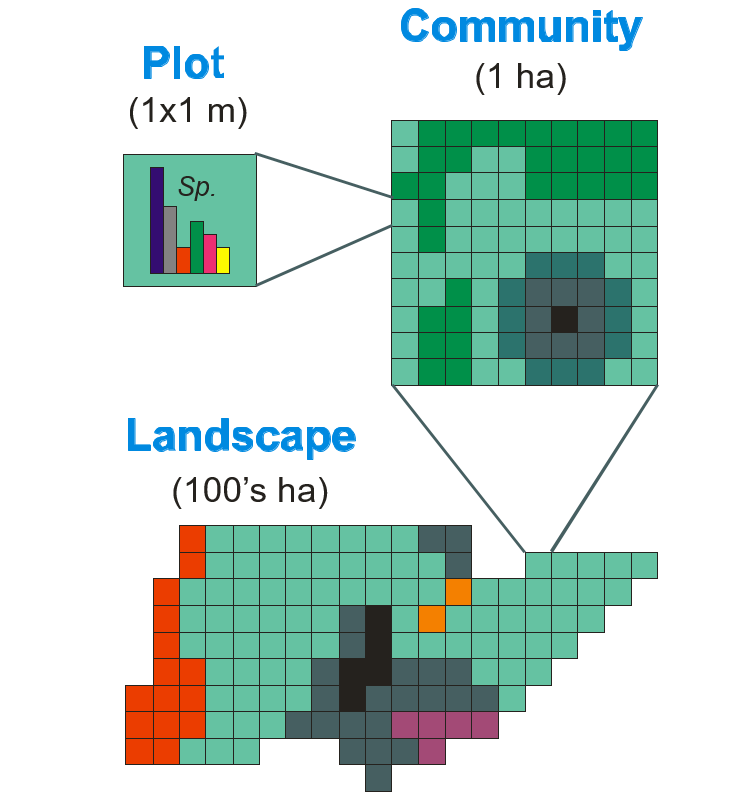
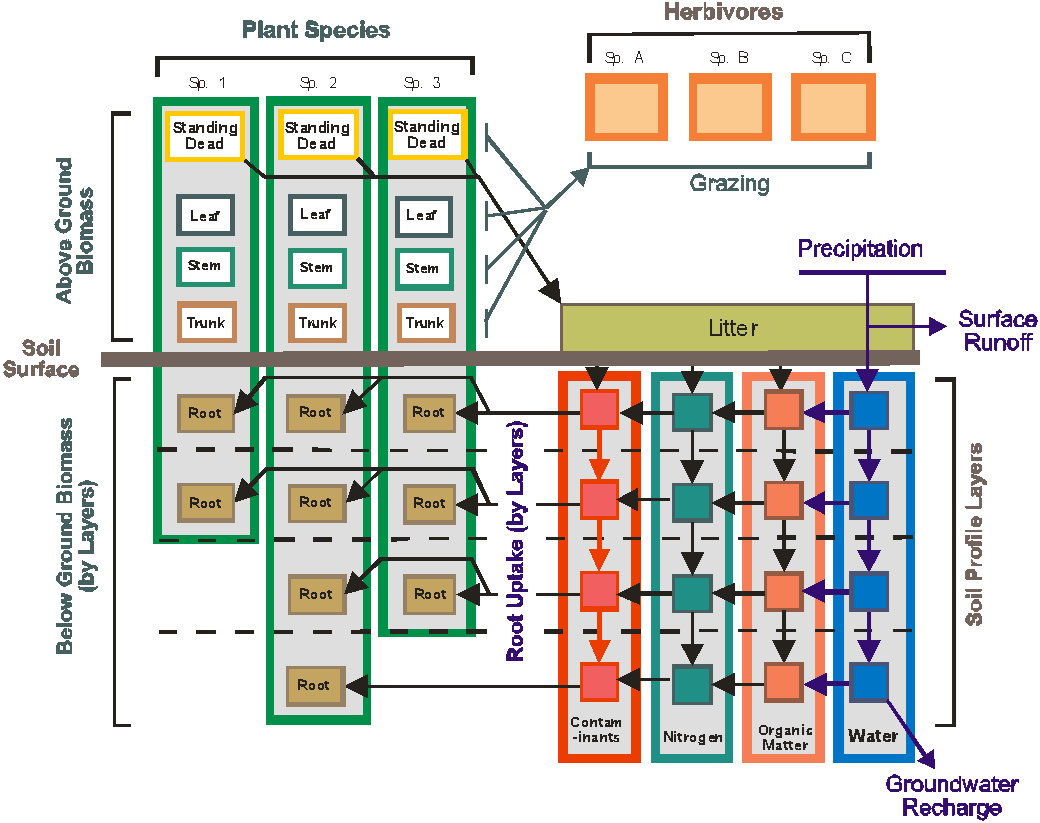
Ecosystem management is hindered by a lack of predictive tools that assess management alternatives under a wide variety of land use and disturbance scenarios. The Ecological DYnamics Simulation (EDYS) model was developed to assist managers in selecting defensible strategies to best meet difficult management objectives, given complex regulatory constraints, and variable climatic and disturbance scenarios. EDYS is a PC-based, mechanistic, spatially-explicit, and temporally-dynamic simulation model designed to mechanistically simulate complex ecological dynamics across spatial scales ranging from plots (square meters) to landscape and watershed (square kilometers) levels. Modules include climatic simulators, hydrology, soil profile, nutrient and contaminant cycles, plant community dynamics, herbivory, animal dynamics, management activities, and natural/anthropogenic disturbances. EDYS has been applied to a variety of ecosystems, from deserts to grasslands, savannas, shrublands, temperate forests, tropical rainforests, and tundra, throughout the western United States, and Indonesia and Australia.
Acknowledgements
I would be remiss if I failed to recognize the contributions of many individuals and organizations. The modeling work detailed on this page was not done solely by me. I had many contributors, but chief among them are Drs. Terry McLendon, Mike Childress, and David Price.
EDYS Locations
Below are the general locations of EDYS applications, followed by a list with more specific information. Entries below include general location, sponsor, date of completion, and a download link if reports or publications are available. Sponsors listed include NPS (National Park Service), NRCS (Natural Resources Conservation Service), SARA (San Antonio River Authority), SERDP (Department of Defense's Strategic Environmental Research and Development Program), TSSWCB (Texas State Soil and Water Conservation Board), USACE (U.S. Army Corps of Engineers), and USFS (U.S. Forest Service). Some EDYS applications and reports contain confidential corporate information and are not currently available to the public. More information on the following projects may be provided upon request.
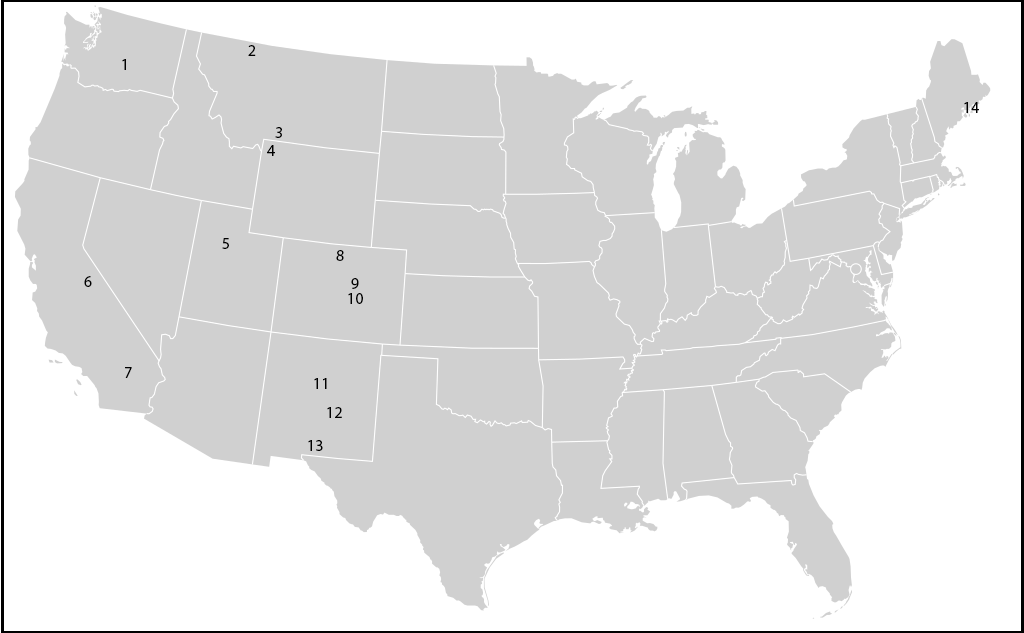
US-1 – Yakima Training Center, Washington – SERDP
Mata-Gonzalez, R., R. G. Hunter, C. L. Coldren, T. McLendon, and M. W. Paschke. 2007. Modelling plant growth dynamics in sagebrush steppe communities affected by fire. Journal of Arid Environments 69:144-157.
Mata-Gonzalez, R., R. G. Hunter, C. L. Coldren, T. McLendon, and M. W. Paschke. 2008. A comparison of modeled and measured impacts of resource manipulations for control of Bromus tectorum in sagebrush steppe. Journal of Arid Environments 72:836-846.
US-2 – Glacier National Park, Montana – NPS, report not available
US-3 – Mineral Hill Mine, Gardiner, Montana
McLendon, T., W. M. Childress, C. L. Coldren, R. Frechette, and F. Bergstrom. 2002. Evaluation of alternative designs for a water-balance cover over tailings at the Mineral Hill Mine, Montana, using the EDYS model. Pages 505-518 in Tailings and Mine Waste '02. A.A. Balkema, publisher.
US-4 – Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming – NPS, report not available
US-5 – Clover Creek Watershed, Utah – NRCS, report not available
US-6 – Owens Valley, California – reports not available
US-7 – 29 Palms Marine Corps Base, California – USACE, report not available
US-8 – Rocky Mountain National Park, Colorado – NPS, report not available
US-9 – Air Force Academy, Colorado – report not available
US-10 – Fort Carson, Colorado – SERDP, report not available
US-11 – Abo Arroyo, New Mexico – report not available
US-12 – Rio Penasco, New Mexico – USFS, report not available
US-13 – Fort Bliss, New Mexico – USACE, 2001
US-14 – Acadia National Park – NPS, report not available
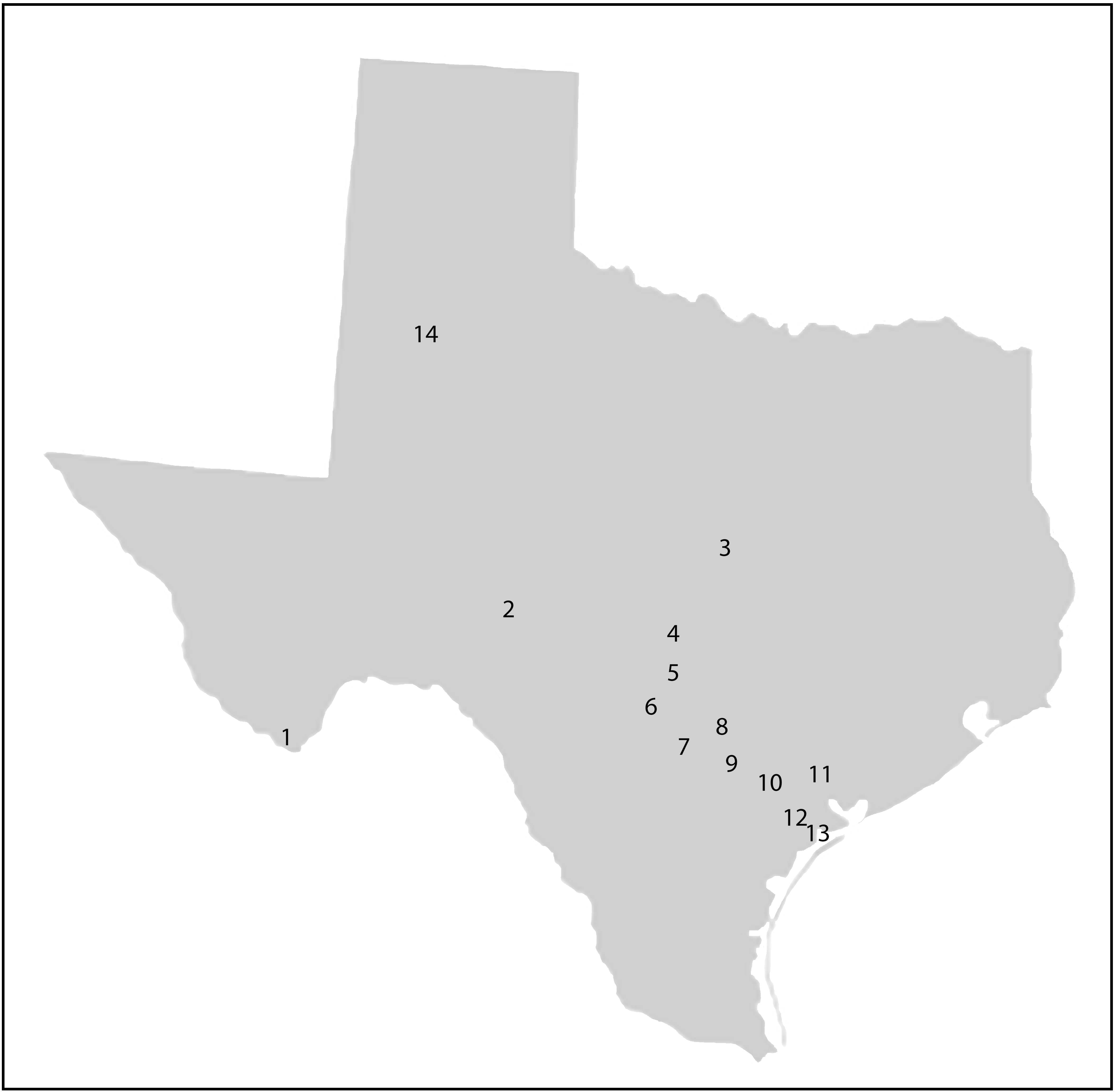
TX-1 – Big Bend National Park – NPS, report not available
TX-2 – Upper Llano River – TSSWCB, 2017
TX-3 – Fort Hood – USACE, 2001
TX-4 – Honey Creek – USACE, 2009
TX-5 – Cibolo Creek – USACE, 2004, 2010
TX-6 – Camp Bullis – USACE, report not available
TX-7 – Wilson County – SARA, 2015
TX-8 – Gonzales County – TSSWCB, 2012
TX-9 – Karnes County – SARA, 2015
TX-10 – Goliad County – SARA and TSSWCB, 2016
TX-11 – Victoria County – SARA and TSSWCB, 2018
TX-12 – Refugio County – SARA, report not yet available
TX-13 – San Antonio Bay – SARA
A. Phase 1 Report – 2012
B. SA Bay Precipitation Report – 2013
C. Phase 2 Report – 2013
D. SA Bay LIDAR Report – 2015
E. EDYS-TxRR Runoff Comparison – 2015
F. EDYS-HSPF Runoff Comparison – 2016
G. SA Bay Validation Sites – 2014, 2018, 2019, 2020
H. Soil Temperature Conceptual Model for EDYS – 2019
I. EDYS-TELEMAC Linkage for Freshwater Inflow Evaluation – 2020
J. Decomposition-Mineralization Conceptual Model for SA Bay – 2020
TX-14 – Lubbock County graduate student research – TTU
Singleton, J. 2019. Role of genetic diversity in the adaptive success of silverleaf nightshade (Solanum elaeagnifolium) under variable environmental pressures. Masters thesis, Texas Tech University. Lubbock, Texas.
Locations Outside the Contiguous 48 States
O-1 – Atigun Pass, Alaska – report not available
O-2 – Island of Sulawesi, Indonesia – report not available
O-3 – Townsville, Australia – CSIRO
Ash, A., and L. Walker. 1999. Environmental management of military lands. Constructing decision support tools to evaluate management alternatives. LWRRDC Project CTC19. Final Report, CSIRO Tropical Agriculture. Aitkenvale, Queensland, Australia.
Other EDYS Documentation
Childress, W. M., D. L. Price, C. L. Coldren, and T. McLendon. 1999. A functional description of the Ecological Dynamics Simulation (EDYS) Model, with applications for army and other federal land managers. U.S. Army Corp of Engineers, CERL Technical Report 99/55.
Childress, W. M., and T. McLendon. 1999. Simulation of multi-scale environmental impacts using the EDYS model. Hydrological Science and Technology 15:257-269.
Childress, W. M., C. L. Coldren, and T. McLendon. 2002. Applying a complex, general ecosystem model (EDYS) in large-scale land management. Ecological Modelling 153:97-108.
Johnson, B. E., and C. L. Coldren. 2006. Linkage of a physically based distributed watershed model and a dynamic plant growth model. U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Vicksburg, Mississippi. Technical Report ERDC/EL TR-06-17.
Coldren, C. L., T. McLendon, W. M. Childress, D. L. Price, and M. R. Graves. 2011. Ecological DYnamics Simulation Model – Light (EDYS-L): User's Guide Version 4.6.4. U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Vicksburg, Mississippi. System-Wide Water Resources Program Final Report ERDC-EL SR-11-1.
Coldren, C. L., T. McLendon, and W. M. Childress. 2011. Ecological DYnamics Simulation Model (EDYS) user's guide, version 5.1.0. KS2 Ecological Field Services, LLC, Fort Collins, Colorado.
Department of Plant and Soil Science
-
Address
Texas Tech University, Department of Plant and Soil Science, Box 42122, Lubbock, TX 79409 -
Phone
806.742.2838 -
Email
plantsoilscience@ttu.edu
